Generalized additive modeling
Martijn Wieling (University of Groningen)
This lecture
- Introduction
- Generalized additive modeling
- Articulography
- Using articulography to study L2 pronunciation differences
- Design
- Methods:
Rcode - Results
- Discussion
Generalized additive modeling (1)
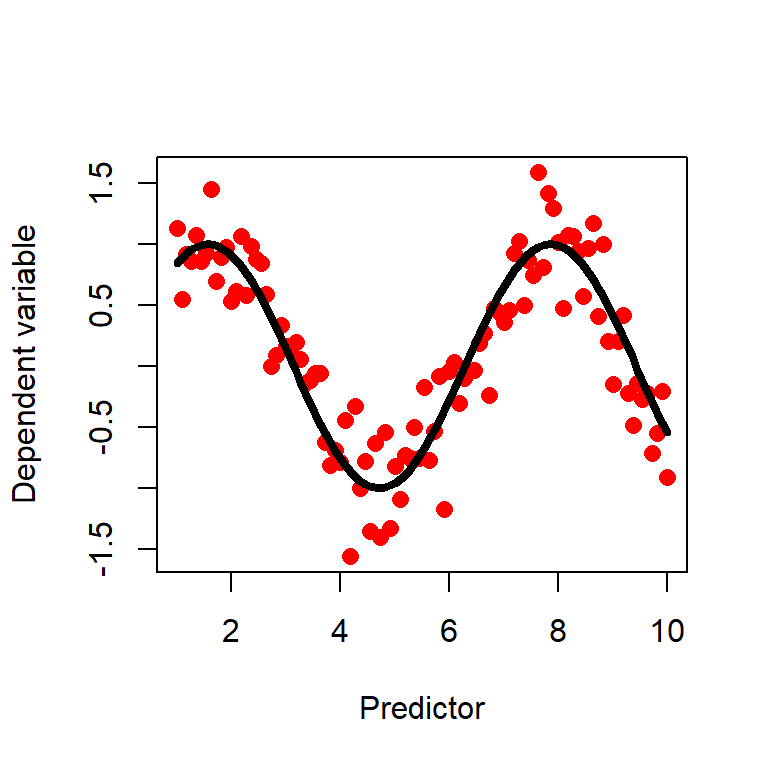
- Generalized additive model (GAM): relaxing assumption of linear relation between dependent variable and predictor
- Relationship between individual predictors and (possibly transformed) dependent variable is estimated by a non-linear smooth function: \(g(y) = s(x_1) +s(x_2,x_3) + \beta_4x_4 + ...\)
- Multiple predictors can be combined in a (hyper)surface smooth (another lecture)
Question 1
Generalized additive modeling (2)
- Advantage of GAM over manual specification of non-linearities: the optimal shape of the non-linearity is determined automatically
- Appropriate degree of smoothness is automatically determined by minimizing combined error and wigglyness (no overfitting)
- Maximum number of basis functions limits the maximum amount of non-linearity
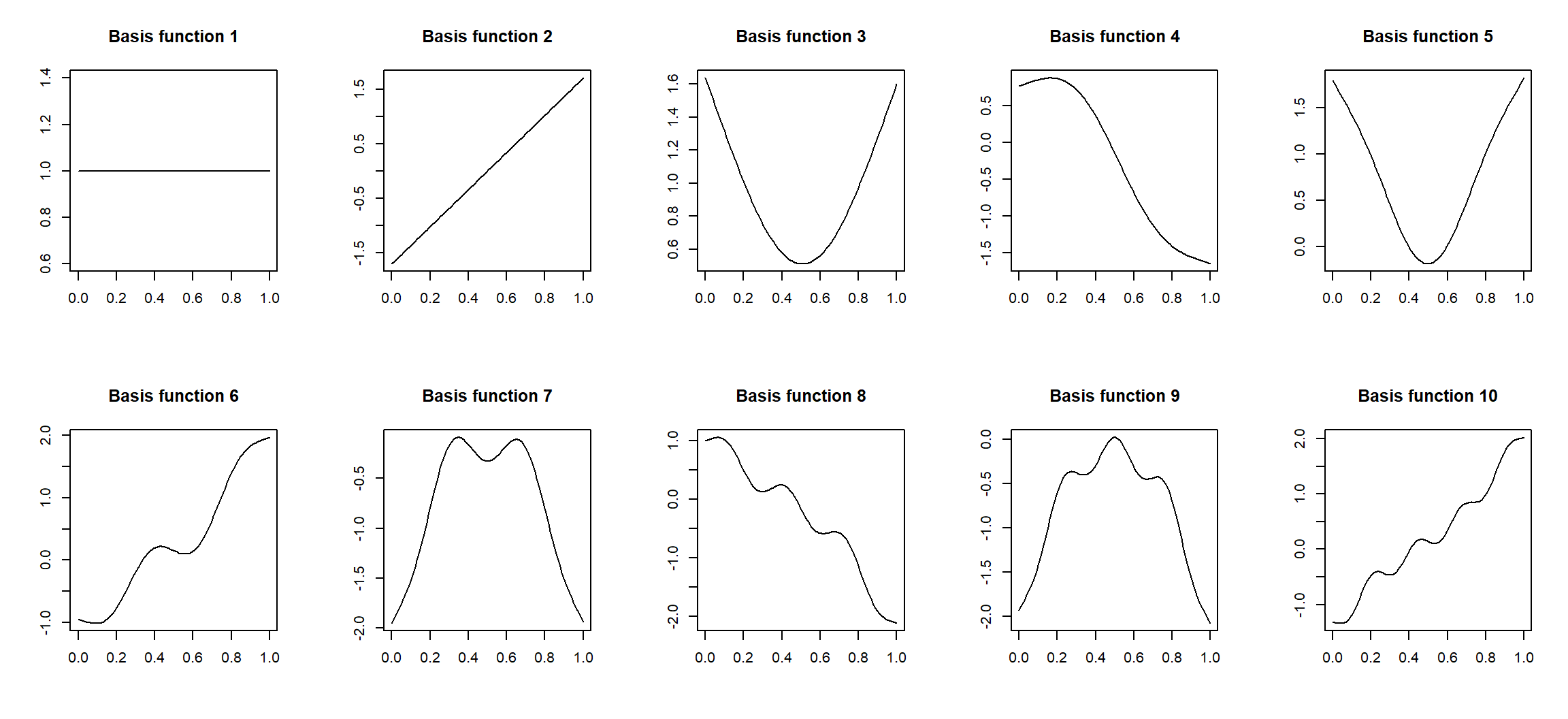
First ten basis functions
Generalized additive modeling (3)
- Choosing a smoothing basis
- Single predictor or isotropic predictors: thin plate regression spline (this lecture)
- Efficient approximation of the optimal (thin plate) spline
- Combining non-isotropic predictors: tensor product spline
- Single predictor or isotropic predictors: thin plate regression spline (this lecture)
- Generalized Additive Mixed Modeling:
- Random effects can be treated as smooths as well (Wood, 2008)
R:gamandbam(packagemgcv)
- For more (mathematical) details, see Wood (2006) and Wood (2017)
Articulography

Obtaining data
Recorded data
Present study: goal and setup
- 19 native Dutch speakers from Groningen
- 22 native Standard Southern British English speakers from London
- Material: 10 minimal pairs [t]:[θ] repeated twice:
- ‘tent’-‘tenth’, ‘fate’-‘faith’, ‘fort’-‘forth’, ‘kit’-‘kith’, ‘mitt’-‘myth’
- ‘tank’-‘thank’, ‘team’-‘theme’, ‘tick’-‘thick’, ‘ties’-‘thighs’, ‘tongs’-‘thongs’
- Note that the sound [θ] does not exist in the Dutch language
- Goal: compare distinction between this sound contrast for both groups
- Preprocessing:
- Articulatory segmentation: gestural onset to offset (within /ə/ context)
- Positions \(z\)-transformed per axis and time normalized (from 0 to 1) per speaker
Data: much individual variation and noisy data
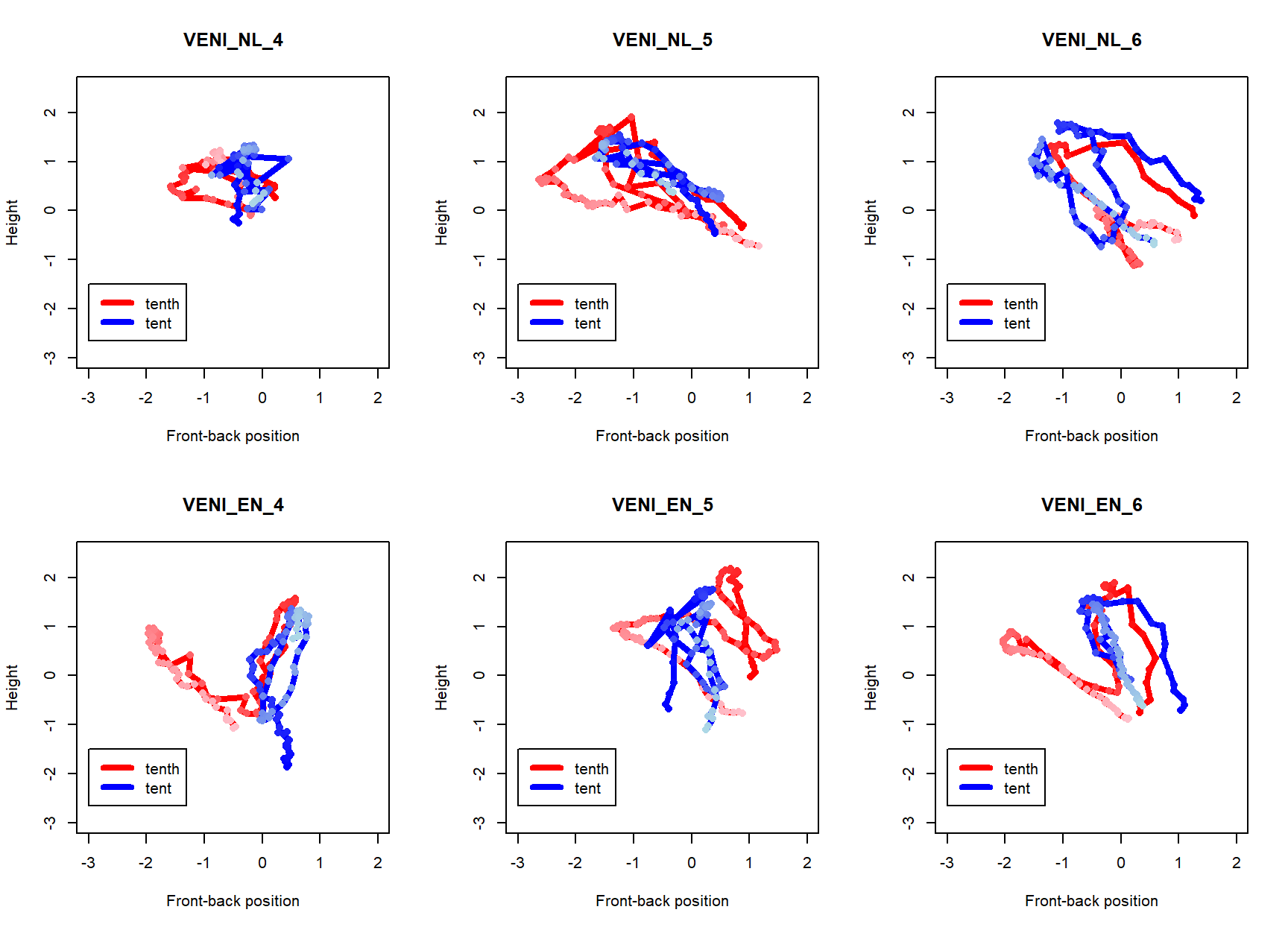
Data overview
Participant Group Word Sound Loc Trial Time TTfront
1 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0000 -0.392
2 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0161 -0.440
3 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0323 -0.440
4 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0484 -0.503
5 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0645 -0.513
6 VENI_EN_1 EN tick T Init 1 0.0806 -0.677[1] 126177 8First model: tongue frontness for “tenth” and “tent”
(R version 4.4.2 (2024-10-31 ucrt), mgcv version 1.9.3, itsadug version 2.4.1)
library(mgcv)
library(itsadug)
tt <- droplevels(full[full$Word %in% c("tenth","tent"),])
# sort data per individual trajectory (necessary to detect autocorrelation)
tt <- tt[order(tt$Participant,tt$Trial,tt$Time),] # sort data per trial
tt$start.event <- tt$Time == 0 # mark the start of every new trial (where Time equals 0)
# fit first GAM
m0 <- bam(TTfront ~ s(Time), data = tt)Model summary
Family: gaussian
Link function: identity
Formula:
TTfront ~ s(Time)
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.40119 0.00825 48.6 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time) 8.4 8.9 170 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
R-sq.(adj) = 0.106 Deviance explained = 10.6%
fREML = 17375 Scale est. = 0.87389 n = 12839Visualizing the non-linear time pattern of the model
(Interpreting GAM results always involves visualization)
Check if number of basis functions is adequate
(if p-value is low and edf close to k’)
Method: fREML Optimizer: perf newton
full convergence after 9 iterations.
Gradient range [-1.25e-07,1.03e-07]
(score 17375 & scale 0.874).
Hessian positive definite, eigenvalue range [3.46,6419].
Model rank = 10 / 10
Basis dimension (k) checking results. Low p-value (k-index<1) may
indicate that k is too low, especially if edf is close to k'.
k' edf k-index p-value
s(Time) 9.0 8.4 1.03 0.98Increasing the number of basis functions with \(k\)
(double \(k\) if higher \(k\) is needed, but not higher than number of data points)
Effect of increasing \(k\)
Individual varation: random effects in lme4 vs. mgcv
(1|Participant):s(Participant, bs="re")(0 + WF|Participant):s(Participant, WF, bs="re")(order may be switched)(1 + WF|Participant): not possible inmgcv
Including individual variation: random intercepts
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.43 0.0648 6.65 3.11e-11 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time) 8.49 8.93 206.1 <2e-16 ***
s(Participant) 40.41 41.00 65.6 <2e-16 ***
Deviance explained = 26.3%- Deviance explained of model without random intercept (\(r^2\)): 10.6%
Effect of including a random intercept
Including individual variation: random slopes
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.431 0.106 4.07 4.72e-05 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time) 8.53 8.94 163 <2e-16 ***
s(Participant) 39.91 41.00 9294 <2e-16 ***
s(Participant,Time) 39.12 41.00 10291 <2e-16 ***
Deviance explained = 31.7%Effect of including a random slope
Including individual variation: factor smooths
(i.e. including a non-linear random effect instead of a random intercept and random slope)
Warning in gam.side(sm, X, tol = .Machine$double.eps^0.5): model has repeated 1-d smooths
of same variable.Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.431 0.0648 6.64 3.22e-11 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time) 8.12 8.48 23.3 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant) 289.74 377.00 16.1 <2e-16 ***
Deviance explained = 40.7%Visualization of individual variation
Effect of including a random non-linear effect
Influence of random effects
Speeding up computation
(via discrete and nthreads, only for default method="fREML")
Comparing “tenth” and “tent” in one model
(smooths are centered, so the factorial predictor also needs to be included in the fixed effects)
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.10 0.0684 1.47 0.142
Wordtenth 0.69 0.0118 58.66 <2e-16 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time):Wordtent 7.28 7.92 9.27 <2e-16 ***
s(Time):Wordtenth 8.51 8.79 42.96 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant) 307.69 377.00 22.54 <2e-16 ***- Does the word distinction improve the model?
Assessing model improvement
(comparing fixed effects, so method='ML' and no discrete=T)
m3.ml <- bam(TTfront ~ s(Time) + s(Time,Participant,bs='fs',m=1), data=tt, method='ML')
m4.ml <- bam(TTfront ~ s(Time,by=Word) + Word + s(Time,Participant,bs='fs',m=1), data=tt,
method = 'ML')
compareML(m3.ml, m4.ml) # model m4.ml is much better!m3.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time) + s(Time, Participant, bs = "fs", m = 1)
m4.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time, by = Word) + Word + s(Time, Participant, bs = "fs",
m = 1)
Chi-square test of ML scores
-----
Model Score Edf Difference Df p.value Sig.
1 m3.ml 15288 5
2 m4.ml 13294 8 1993.462 3.000 < 2e-16 ***
AIC difference: 4105.95, model m4.ml has lower AIC.Visualizing the two patterns
Visualizing the difference
Question 2
Including individual variation for “tenth” vs. “tent”
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.118 0.0947 1.25 0.213
Wordtenth 0.622 0.1181 5.27 1.41e-07 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time):Wordtent 7.56 7.97 9.6 <2e-16 ***
s(Time):Wordtenth 8.40 8.56 22.5 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtent 316.62 377.00 38.0 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtenth 328.46 368.00 43.1 <2e-16 ***- This approach is overly conservative when determining the (tenth-tent) difference
- An alternative approach is introduced in another lecture
More uncertainty in the difference
Autocorrelation in the data is a problem!
(residuals should be independent, otherwise the standard errors and p-values are wrong)
- See also supplementary material
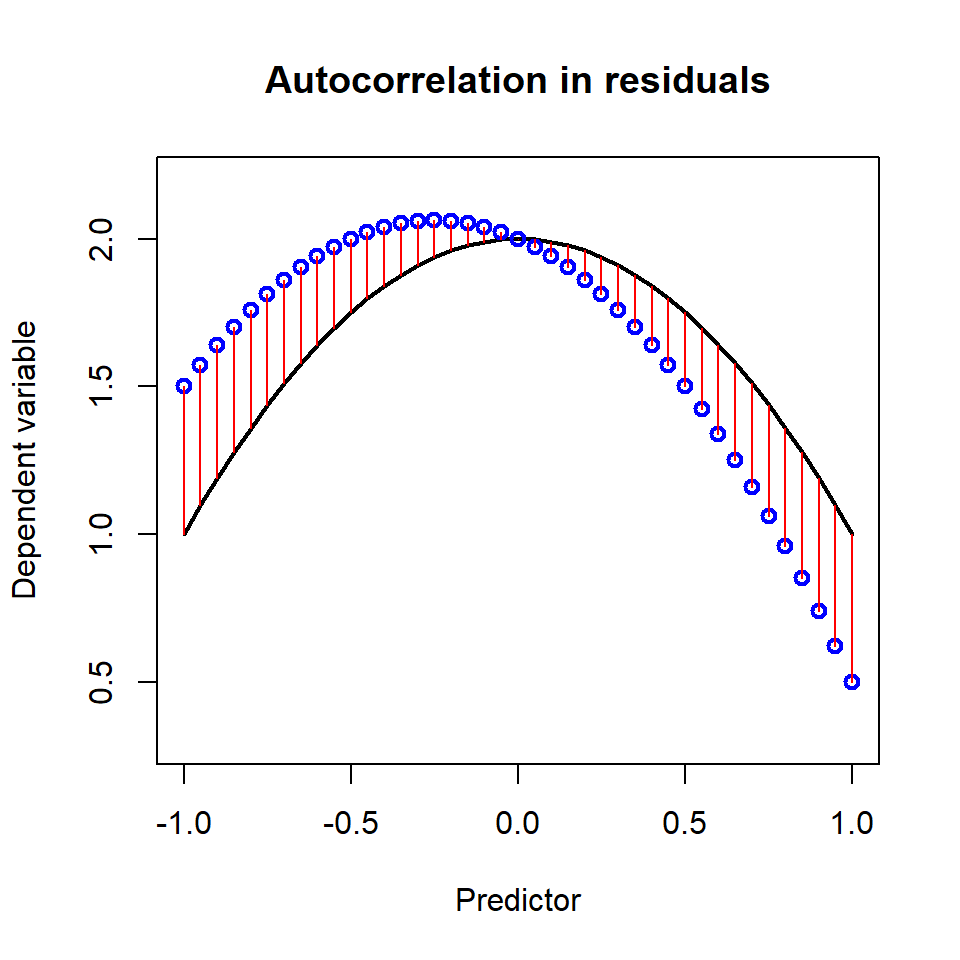
Correcting for autocorrelation
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.118 0.090 1.31 0.192
Wordtenth 0.623 0.113 5.51 3.66e-08 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time):Wordtent 7.42 8.09 8.94 <2e-16 ***
s(Time):Wordtenth 8.31 8.59 21.77 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtent 229.53 377.00 2.84 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtenth 269.34 368.00 3.81 <2e-16 ***Autocorrelation has been removed
Clear model improvement
m5.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time, by = Word) + Word + s(Time, Participant, by = Word,
bs = "fs", m = 1)
m6.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time, by = Word) + Word + s(Time, Participant, by = Word,
bs = "fs", m = 1)
Model m6.ml preferred: lower ML score (12679.727), and equal df (0.000).
-----
Model Score Edf Difference Df
1 m5.ml 9381 10
2 m6.ml -3298 10 -12679.727 0.000
AIC difference: 24349.22, model m6.ml has lower AIC.Question 3
Random effects and autocorrelation
Distinguishing the two speaker groups
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -0.065 0.120 -0.54 0.588
WordGrouptenth.EN 0.744 0.152 4.89 1e-06 ***
WordGrouptent.NL 0.385 0.175 2.21 0.027 *
WordGrouptenth.NL 0.879 0.157 5.59 2.3e-08 ***
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time):WordGrouptent.EN 3.88 4.59 2.32 0.041 *
s(Time):WordGrouptenth.EN 7.93 8.35 15.82 <2e-16 ***
s(Time):WordGrouptent.NL 7.46 8.14 10.85 <2e-16 ***
s(Time):WordGrouptenth.NL 7.72 8.19 11.87 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtent 218.20 377.00 2.62 <2e-16 ***
s(Time,Participant):Wordtenth 256.81 369.00 3.43 <2e-16 ***Visualizing the patterns
(note that the difference curves are overly conservative)
plot_smooth(m7, view='Time', rug=F, plot_all='WordGroup', main='m7', ylim=c(-1,2))
plot_diff(m7, view='Time', comp=list(WordGroup=c('tenth.EN','tent.EN')), main='EN difference', ylim=c(-1,2))
plot_diff(m7, view='Time', comp=list(WordGroup=c('tenth.NL','tent.NL')), main='NL difference', ylim=c(-1,2))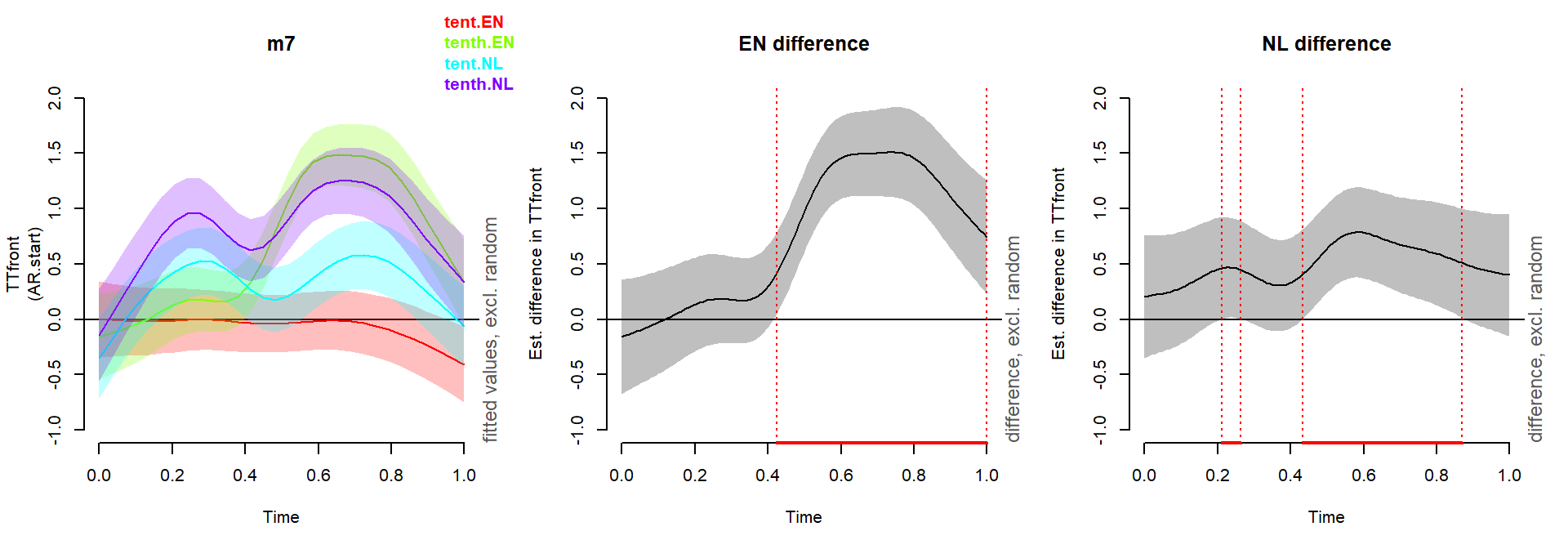
Including language is necessary
m6.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time, by = Word) + Word + s(Time, Participant, by = Word,
bs = "fs", m = 1)
m7.ml: TTfront ~ s(Time, by = WordGroup) + WordGroup + s(Time, Participant,
by = Word, bs = "fs", m = 1)
Chi-square test of ML scores
-----
Model Score Edf Difference Df p.value Sig.
1 m6.ml -3298 10
2 m7.ml -3314 16 15.218 6.000 3.247e-05 ***
AIC difference: 4.51, model m7.ml has lower AIC.The full tongue tip model: all words
(Word is now a random-effect factor, Sound distinguishes T from TH words)
full$SoundGroup <- interaction(full$Sound,full$Group)
# alternative function (from itsadug) for sorting and generating start.event column
full <- start_event(full, event=c("Participant","Trial"))
# duration discrete=F: 155 sec., discrete=T: 29 s. (1 thr.) / 16 s. (2 thr.)
system.time(model <- bam(TTfront ~ s(Time,by=SoundGroup) + SoundGroup +
s(Time,Participant,by=Sound,bs='fs',m=1) +
s(Time,Word,by=Group,bs='fs',m=1),
data=full, rho=rhoval, AR.start=full$start.event,
discrete=T)) user system elapsed
29.47 0.37 30.05 The full tongue tip model: results
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -0.002 0.132 -0.01 0.988
SoundGroupTH.EN 0.699 0.201 3.48 0.000509 ***
SoundGroupT.NL 0.180 0.216 0.84 0.404
SoundGroupTH.NL 0.509 0.229 2.22 0.026 *
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df F p-value
s(Time):SoundGroupT.EN 5.16 5.50 2.96 0.014 *
s(Time):SoundGroupTH.EN 6.61 6.86 6.55 3.04e-06 ***
s(Time):SoundGroupT.NL 7.25 7.45 4.38 3.12e-05 ***
s(Time):SoundGroupTH.NL 6.91 7.13 5.95 5.52e-06 ***
Deviance explained = 53.5%L1-based differences
(note that the CIs of the difference curves are overly conservative)
Discussion
- Native English speakers appear to make the /t/-/θ/ distinction, whereas Dutch L2 speakers of English generally do not
- But this does not necessarily mean the difference between these distinctions is significant (see this tutorial; Wieling, 2018)
- The approach used in this lecture to model non-linear random effects yielded overly conservative difference smooths
- In this lecture about GAMs, a better approach is explained
Question 4
How to report?
- For an example of how to report this type of analysis, see:
- Wieling (2018), Journal of Phonetics: GAM tutorial (paper package: data and code)
- Wieling et al. (2016), Journal of Phonetics (paper package: data and code)
Recap
- We have applied GAMs to articulography data and learned how to:
- use
s(Time)to model a non-linearity over time - use the
kparameter to control the number of basis functions - use the plotting functions
plot_smoothandplot_diff - use the parameter setting
bs='re'to add random intercepts and slopes - add non-linear random effects using
s(Time,…,bs='fs',m=1) - use the
by-parameter to obtain separate non-linearities- Note that this factorial predictor also needs to be included in fixed effects!
- use
compareMLto compare models (comparing fixed effects:method='ML')
- use
- Associated lab session:
Evaluation
Questions?
Thank you for your attention!
https://www.martijnwieling.nl
m.b.wieling@rug.nl











