

Next: Transfer model Up: Views on Translation Previous: Linguistically possible translation
Symmetry
Since `possible translation' is defined in terms of `having the
same syntactic meaning', the relation is symmetric. That is,
for each pair of sentences 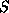 and
and 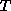 ,
, 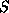 translates to
translates to 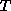 if and
only if
if and
only if 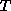 translates to
translates to 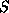 . Because we preserve the syntactic
structure only to a certain degree (wherever possible), we suspect that
the relation is not transitive.
. Because we preserve the syntactic
structure only to a certain degree (wherever possible), we suspect that
the relation is not transitive.
Given the assumption that linguistically possible translation is a symmetric relation, we have defined the computational model in such a way that it is reversible (see below).
Gertjan van Noord
Thu Nov 24 18:57:05 MET 1994