

Next: Minimization
Up: Operations on recognizers
Previous: Determinization
If the determinizer also maintains the empty subset of
states (cf. the last line in the previous example), then the resulting
determinized automaton is complete: for each state a transition is
applicable for each symbol of the alphabet. This property is important
in order to define complementation. If an automaton M1 with final
states  is deterministic and complete, then an automaton
accepting the language
is deterministic and complete, then an automaton
accepting the language
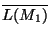 is obtained from M1 simply by
replacing F with Q-F.
is obtained from M1 simply by
replacing F with Q-F.
As usual, the difference operation is defined straightforwardly in
terms of complementation and intersection: if A and B are regular
languages, then A-B is defined as
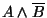 .
.
Noord G.J.M. van
2001-06-22
![]() .
.