

Next: Robust Parsing
Up: Dependency Structures
Previous: Dependency Treebanks.
Evaluation of coverage and accuracy of a computational grammar usually
is based on some metric which compares tree structures (such as recall
and precision of (labelled) brackets or bracketing inconsistencies
(crossing brackets) between test item and parser output). As
is well-known, such metrics have a number of drawbacks.
Therefore, [7] propose to annotate
sentences with triples of the form 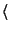 head-word, dependency
relation, dependent head-word
head-word, dependency
relation, dependent head-word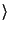 . For
instance, for the example in (1) we might obtain:
. For
instance, for the example in (1) we might obtain:
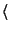 zou, su, mercedes zou, su, mercedes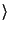 |
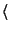 aangekondigd, obj1, model aangekondigd, obj1, model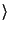 |
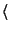 hebben, su, mercedes hebben, su, mercedes |
 model, det, haar model, det, haar |
 aangekondigd, su, mercedes aangekondigd, su, mercedes |
 model, mod, nieuwe model, mod, nieuwe |
 aangekondigd, mod, gisteren aangekondigd, mod, gisteren |
|
Dependency relations between head-words can be extracted easily from
the dependency structures in our treebank, as well as from the dependency
structures constructed by the parser. It is thus straightforward
to compute precision, recall, and f-score on the set of
dependency triples.
Noord G.J.M. van
2001-05-15