

Next: Implementation Up: Overview of the Previous: Reversible Unification Grammars
Morphology
The monolingual components of the formalism thus consist of
unification grammars, similar to PATR.
Unlike PATR the terminal elements in the formalism are
not defined in the lexicon, but orthographical, inflectional and
morphological rules define the relation between the terminals and
a lexicon of stems and affixes. For example, the word `eaters'
is analyzed into [eat,er,s] by the orthographical component. For
the orthographical component we use a reversible two-level system
[37][6][25].
Reversible inflectional rules relate to 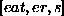 a list of stems and
affixes
a list of stems and
affixes 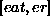 with the feature structure
with the feature structure 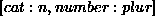 .
Inflection is defined by a formalism comparable to the
paradigmatic approach of [8].
Morphological
analysis is based on a separate reversible unification grammar in which derivational
processes and compounding can be defined [4]. For example,
.
Inflection is defined by a formalism comparable to the
paradigmatic approach of [8].
Morphological
analysis is based on a separate reversible unification grammar in which derivational
processes and compounding can be defined [4]. For example,
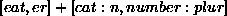 could be analysed as
could be analysed as 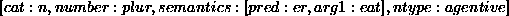 . Note
that the separation of inflectional rules and compound/derivation
rules implements a type of `level' theory defended by e.g. [2].
. Note
that the separation of inflectional rules and compound/derivation
rules implements a type of `level' theory defended by e.g. [2].
Gertjan van Noord
Thu Nov 24 19:09:23 MET 1994